In the vast realm of manufacturing and machining, the lathe machine stands out as a pivotal tool with a rich history and a spectrum of applications that have shaped industries for centuries. “Lathe Machine Definition, Types, Hazards, and Control Measures” delves deep into the multifaceted world of lathes, offering readers an in-depth understanding of its core definition, the diverse types available, and the potential hazards associated with its operation.
More importantly, this blog underscores the quintessential control measures to mitigate these hazards, ensuring both efficiency and safety in the workplace. Whether you’re a seasoned machinist, a student of engineering, or simply curious about the intricacies of machinery that powers our modern world, this guide will provide valuable insights and essential knowledge. Dive in and discover the dynamic world of lathe machines!
Lathe Machine Definition
A lathe machine is a versatile and ancient tool, pivotal in the world of machining. It works by rotating a workpiece on its axis, allowing for operations like cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, or deformation to produce symmetrical objects with precision. Originating thousands of years ago, the lathe’s fundamental principle has remained relatively unchanged. Over the millennia, it has been employed to craft items ranging from small, intricate pieces like coins and jewelry to larger, functional items like furniture components and sculptures.
In today’s modern manufacturing and engineering landscape, the lathe continues to hold an indispensable position. Its applications span numerous industries, reflecting its adaptability and essential nature. In the automotive sector, for example, lathes are utilized to fashion crucial components with tight tolerances. The aerospace industry relies on them to produce parts that must withstand extreme conditions, while the medical field uses lathes to create intricate instruments and implants. As technology advances, so does the sophistication and capability of the lathe, ensuring its place in the annals of indispensable tools.

History Of Lathe Machine
With its rich heritage, the lathe stands tall as one of the most fundamental and ancient machine tools. Often dubbed “the mother of all machine tools,” its inception laid the groundwork for the principles behind many other machine tools that came after it.
Tracing back its lineage, the rudimentary forms of the lathe appeared as early as 2000 BC, with the Egyptians pioneering its use to craft wooden bowls and similar items. Subsequent civilizations, like the Romans, also embraced the lathe, harnessing its capabilities for crafting an array of artifacts, from statues to furniture. The dawn of the Industrial Revolution marked a pivotal chapter in its history, as lathes played a significant role in manufacturing parts for an array of burgeoning machinery. In our contemporary era, the lathe continues to be indispensable, underpinning myriad manufacturing and production endeavors.
Milling Machines Vs. Lathe Machines
Milling and lathe machines, though both integral in the machining world, serve distinct purposes and functions based on different principles. At their core, milling machines employ rotary cutters to remove material from a stationary workpiece. They are incredibly versatile, adept at handling various tasks, and especially advantageous when dealing with intricate or large-scale objects. Their designs allow for multi-axis movement, which provides the flexibility to produce complex geometries.
Lathes, conversely, operate by rotating the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool. This design is ideal for tasks that require symmetrical operations around a central axis. Typically, lathes excel at producing cylindrical or round objects and are especially prized for the precision and detail they can achieve, particularly for smaller components. While milling machines are versatile powerhouses for large and complex tasks, lathe machines deliver precision and detail on smaller, often round objects.
Lathe Machine Working Principles
At its core, a lathe machine is designed to rotate a workpiece around its axis. This is achieved using a motor that drives a central spindle. Once the workpiece is secured to the spindle, its rotation enables cutting, grinding, or shaping by stationary tools that come into contact with it. Operators can adjust the rotation speed based on the task’s requirements.
Furthermore, the direction of rotation can be toggled, which provides versatility in the machining process. The essence of a lathe’s operation is this controlled rotation, which enables the crafting of diverse objects with symmetrical features.
Lathe Machine Parts & Functions
- Bed: This is the backbone of the lathe machine, offering a solid and stable base. It ensures that all other components are aligned and supported. The bed’s rigidity is vital for the machine’s accuracy and precision.
- Headstock: Situated on one end of the bed, the headstock is the power hub of the lathe. Within the headstock lies the motor, which drives the spindle, and, consequently, determines the rotation speed of the workpiece. It’s here that the main rotational force is generated.
- Tailstock: Positioned on the bed’s opposite end from the headstock, the tailstock primarily offers support. The tailstock provides the counter-support for longer workpieces that could wobble or become unstable during operation, ensuring that the workpiece remains centered and stable.

Types Of Lathe Machine
There are several different types of lathe machines, each designed for a specific purpose. The most common types of lathes are:
- Turret Lathe Machine
- Speed Lathe Machine
- Engine Lathe Machine
- CNC Lathe Machine
- Tool Room Lathe Machine
- Bench Lathe Machine
- Wood Lathe Machine
1. Turret Lathe Machine
A Turret Lathe Machine is renowned for its versatility and precision. It is an advanced tool often called CNC Turret Lathe or Swiss Type CNC Lathe. What sets this machine apart is its ability to produce large and intricate parts with varying shapes, from simple threads on screws to more complex components like gears and pulleys.
As its name suggests, it operates using a Computer Numerical Control (CNC) system, where the operator provides the desired specifications, and the system then auto-generates the code to shape the part. This method allows for high precision and speed, making it invaluable for industries requiring intricate machined parts.
2. Speed Lathe Machine
As the name implies, the Speed Lathe Machine is a powerhouse regarding speed and efficiency. Also known as CNC lathes or Computer Numerical Control lathes, these machines work under the guidance of computerized controls. Their primary advantage is the rapid production capability combined with a high degree of precision.
Industries that require bulk production in a limited timeframe benefit the most from Speed Lathe Machines. While they offer many benefits, they come with a heftier price tag and the need for regular maintenance, which might make them a significant investment for some businesses.
3. Engine Lathe Machine
The Engine Lathe Machine is a versatile tool primarily designed for creating or refining cylindrical objects. Operated by skilled machinists, it comes with many attachments, each designed for specific tasks. For instance, a chuck is utilized for gripping the workpiece securely during the machining process.
Other essential components include the tailstock for stabilizing the workpiece and the tool post to hold various cutting tools. Engine lathes are celebrated for the diverse finishes they can impart, ranging from smooth surfaces to rough or textured finishes.
4. CNC Lathe Machine
Distinct from other lathes, the CNC Lathe Machine is a marvel of modern engineering. It operates using computerized controls, enabling the creation of intricate and precise parts. These machines are particularly prevalent in the manufacturing processes of smaller to medium-sized products, offering more consistency and accuracy than their traditional counterparts. A significant advantage is the ease of operation and faster production times, making them a favorite in many industries.
5. Tool Room Lathe Machine
The Tool Room Lathe Machine is the go-to choice for workshops that prioritize precision above all. Specifically designed for high accuracy, these lathes might not offer the versatility seen in other lathes but compensate with unmatched precision. They are an indispensable asset in workshops that deal with detailed, precise work, ensuring that every piece turned out is of the highest quality.
6. Bench Lathe Machine
Compact and convenient, the Bench Lathe Machine is perfect for smaller tasks. As the name suggests, it’s designed to be placed on workbenches or tabletops. Although these lathes might not possess the power or precision of their larger counterparts, they are perfect for small projects and are an excellent choice for hobbyists or workshops with space constraints.
7. Wood Lathe Machine
Designed specifically for woodworking, the Wood Lathe Machine is essential for crafting various wooden objects. From shaping to smoothing, this machine has a wide range of applications. The most common projects undertaken on a wood lathe include crafting bowls, vases, and other symmetrical objects.
With adjustable motor speeds to cater to different wood types and requirements, wood lathes are a favorite among woodworkers, from novices to seasoned professionals. Whether the goal is to produce functional items or purely decorative pieces, a wood lathe machine proves indispensable.

Lathe Safety Devices
Understanding the potential dangers and implementing safety measures is paramount when working with lathes. Let’s explore the essential safety devices and their roles in ensuring a safe working environment for lathe operators:
- Lathe Guards: These protective barriers shield the operator from the lathe’s moving parts, especially the rotating components. They’re crucial because they prevent direct contact, which could lead to severe injuries. Ensuring these guards are correctly positioned is vital; while they should offer protection, they mustn’t hinder the operator’s ability to work efficiently.
- Emergency Stop Buttons: Recognizing the need for an immediate cessation of a machine’s operation is behind installing emergency stop buttons on lathes. These buttons are strategically placed to be within easy reach of the operator. If something goes awry or there’s a sudden recognition of a potential hazard, hitting this button will immediately halt the lathe’s function, potentially preventing accidents.
- Chuck Keys: These are specialized tools for tightening or loosening the chuck holding the workpiece. However, one vital safety note is that the chuck key should always be removed after adjusting the chuck. Leaving it inserted while the lathe is in operation can be a significant hazard as the key can be flung out at high speeds, causing injuries.
- Lathe Tools: The tools used for cutting and shaping materials on the lathe must be in optimal condition. Regularly inspecting them for wear and ensuring they’re sharp is vital. Dull or damaged tools lead to poor work quality and pose significant dangers, such as unexpected kickbacks, which can harm the operator.
- Machine Lights: Visibility is a crucial aspect of safe machine operation. Machine lights, often adjustable, illuminate the work area, allowing the operator to see their work and any potential issues. Working under adequately lit conditions minimizes the chances of mistakes and helps detect any irregularities in the work process.
Incorporating and maintaining these safety devices and measures is essential for the safety of lathe operators. They ensure the operator’s well-being and contribute to better efficiency and product quality.
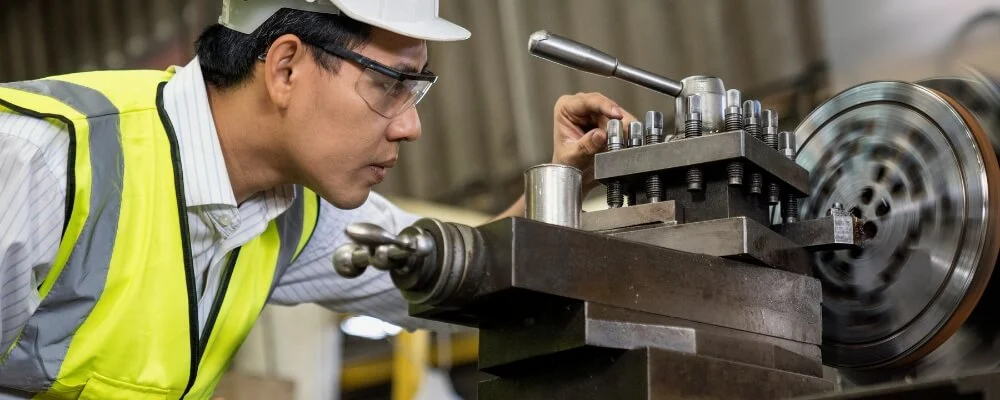

Lathe Machine Hazards and Safety Controls
Working on a lathe machine can be dangerous if the proper safety controls are not in place. There are several hazards associated with operating a lathe machine, including:
1. Struck By Flying Debris
Turning materials on a lathe often subjects them to significant stresses, and not all materials respond the same way. Materials with flaws, imperfections, or simply the nature of some tasks can cause pieces to fracture and dislodge. When these pieces break away, the rotation speed of the lathe can propel them with great force. This makes them potentially lethal projectiles that can cause injuries ranging from superficial cuts to more severe trauma, especially if they strike sensitive areas like the eyes or face.
It’s more than just the immediate danger of injury, as such incidents can also distract the operator, leading to additional mishaps. Thus, wearing protective equipment such as safety goggles or face shields is not just recommended but essential. These tools are designed to withstand impacts and protect the user from flying debris, ensuring the operator remains unharmed even if fragments fly off.
2. Hit By The Chuck
The chuck serves as the anchor point for materials on the lathe, gripping them tightly so they can be worked on without movement. However, this integral component has its dangers. It can come loose if the chuck becomes improperly secured due to wear and tear, mechanical failure, or oversight. In scenarios where it detaches entirely while the lathe is operational, it becomes a heavy, rapidly spinning object with significant potential for harm.
Considering the weight and rotation speed, a dislodged chuck can result in severe injuries or even fatalities. To avoid such dire consequences, it’s crucial for operators to regularly inspect the chuck’s integrity and secure fit before starting the lathe. Furthermore, maintaining a safe distance and being cautious not to reach near it during operation can further reduce risk.
3. Machine Entanglement
The nature of lathes, with their continuous rotation and multiple moving parts, introduces the risk of entanglement. Something as simple as a loose shirt sleeve, a dangling necklace, or untied hair can get caught in the machine. When this happens, the outcome can be devastating. The force exerted by the machine can pull the operator in, leading to possible fractures, dislocations, or worse.
Beyond the immediate physical injuries, such incidents can also result in long-term psychological trauma. The simple act of wearing appropriate attire—clothing that fits closely to the body without loose ends—can dramatically decrease entanglement risks. Similarly, securing long hair in a bun or under a cap and avoiding jewelry can ensure safety.
4. Electrocution
If compromised, the electrical components powering a lathe can pose a life-threatening risk. Damaged cords, exposed wires, or even moisture infiltration can create a conduit for electrical currents to reach the operator. The human body is a good conductor of electricity, and an electric shock can lead to severe injuries, cardiac arrest, or even death. The nuances of electrical safety can’t be overstated.
Regular inspections are essential to check the integrity of wires, connections, and other electrical components. Proper insulation ensures that the risk of electrocution is minimized even if there’s a fault. Furthermore, keeping the working environment dry, free from spills or moisture, can prevent unintended paths for electrical currents.
5. Falling Objects
Due to their design and operation, lathes can sometimes cause parts of the workpiece to fly off and fall downward. These falling objects, depending on their size, weight, and the height from which they fall, can cause injuries. The nature of these injuries can range from minor bruises to significant trauma, especially if the fallen object is sharp or heavy. Moreover, such incidents can also damage the workshop floor or other equipment nearby.
Maintaining a clean and organized workspace can make it easier to spot potential risks before they become hazards. Ensuring the workpiece is clamped securely and stable before starting the lathe can reduce the risk of parts breaking away and falling. Regularly checking and replacing worn-out components that secure the workpiece can ensure that everything remains in place during operation.

6. Crushing Hazards
Lathes, with their powerful rotation and mechanical grip, have areas that pose potential crushing dangers. The most notable is the space between the chuck, which holds the workpiece, and the lathe bed. As the lathe operates, tremendous force is exerted within this area. The results can be catastrophic if an operator inadvertently places their fingers, hands, or body parts within this zone.
Injuries can range from bruises and bone fractures to severe crush injuries that may necessitate medical surgeries or amputations. This aspect of lathe operation highlights the vital need for operators to always be mindful of their hand placements, ensuring they maintain a safe distance from any moving parts of the machine. Additionally, regular training sessions emphasizing this danger can instill a heightened sense of caution among operators.
7. Shearing Hazards
The very essence of a lathe’s function is to shear material off a workpiece. Often sharp and robust, the cutting tool interacts with the rotating workpiece at high speeds, shearing off material to shape it. While vital for the machine’s operation, this powerful shearing action is also a potential hazard.
If an operator’s hand or finger gets caught between the cutting tool and the workpiece, the injury can be severe, with possibilities of deep cuts or even full severance. Awareness of one’s hand placement and movements is paramount. Furthermore, ensuring that the cutting tools are securely fixed and not wobbly can prevent unexpected movements that could lead to accidents.
8. Flying Objects
While flying debris primarily refers to fragments of the workpiece, there’s also the risk associated with other objects near the lathe. Tools, machine accessories, or any loose items can get caught in the machine’s rotation if inadvertently placed too close. When this happens, these objects can be flung with considerable force, posing risks similar to flying debris.
Injuries can range from minor to severe, depending on the object’s size, weight, and speed at which it’s thrown. As with flying debris, wearing protective eyewear is crucial. Maintaining a clutter-free workspace and ensuring no extraneous items are near the lathe can further reduce this risk.
9. Moving Parts
A lathe is a symphony of moving parts, each playing a role in shaping, cutting, and refining a workpiece. However, these moving parts, from the chuck’s rotation to the tool post’s movement, present potential dangers. An accidental touch or a misplaced hand can lead to cuts, bruises, scrapes, or more severe injuries.
It’s not just about the risk of entanglement but also about the harm that can come from simple contact. Ensuring that operators are well-trained and always aware of the machine’s movements. Moreover, any safety guards or protective devices that come with the lathe should always be in place and functional. These barriers keep operators safe from accidental contact with moving parts.
10. Improperly Secured Workpiece
The starting point of any lathe operation is securing the workpiece. If this fundamental step is compromised, the risks escalate exponentially. An improperly secured workpiece can wobble, leading to uneven cuts. It can be dislodged entirely in the worst-case scenario, becoming a dangerous projectile.
Beyond the direct risks posed by the workpiece itself, an unsteady piece can also cause the cutting tool to break or the machine to malfunction. Operators should always double-check the workpiece’s secure placement to avoid these hazards. Regular maintenance and inspections of the chuck and other securing mechanisms are also crucial to ensure optimal working conditions.
Additional Lathe Machine Hazards and Controls Measures
- Unbalanced Workpiece: An uneven or unbalanced workpiece can cause the lathe to vibrate excessively or operate unpredictably. This can be both damaging to the machine and dangerous for the operator. Proper mounting and alignment are crucial.
- Cutting Tool Chatter: This occurs when the cutting tool vibrates, leading to uneven cuts and potentially causing the tool to break or the workpiece to become dislodged. Ensuring tools are sharp and securely mounted can prevent this.
- Vibration: Excessive vibration in a lathe can lead to poor work quality and may cause machine parts to loosen over time. Ensuring the lathe is well-maintained and anchored can reduce vibrations.
- Noise: Lathes can be loud, and consistent exposure to high noise levels can harm hearing. Regular maintenance and lubrication can reduce noise levels, but operators should also consider wearing ear protection.
- Heat: Friction from the machining process can generate heat, posing a burn risk. Proper cooling methods and wearing gloves can help manage this hazard.
- Dust: Some materials can produce dust when machined. Inhaling this dust can be harmful. Keeping the lathe clean and using appropriate ventilation or masks can help reduce this risk.
- Electrical Hazards: Beyond electrocution, electrical problems can lead to fires or damage to the machine. Ensuring the lathe is properly grounded and regularly inspected is essential.
- Fire Hazards: Sparks, excessive heat, or electrical issues can cause fires. Ensuring the workspace is well-ventilated and free of flammable materials is crucial.
- Explosion Hazards: Certain materials or conditions might lead to explosive scenarios. Having spark arrestors and working in a well-ventilated area can reduce this risk.
- Chemical Hazards: Lubricants, coolants, or the materials being worked on can introduce chemical hazards. Proper handling, storage, and protective equipment are key to safety.
- Radiation Hazards: Some machining processes may produce ultraviolet or infrared radiation. Proper shielding and protective eyewear can help protect against this.
- Biological Hazards: Materials, especially if organic or untreated, can introduce biological risks. Regular cleaning and, if necessary, disinfection can mitigate these hazards.
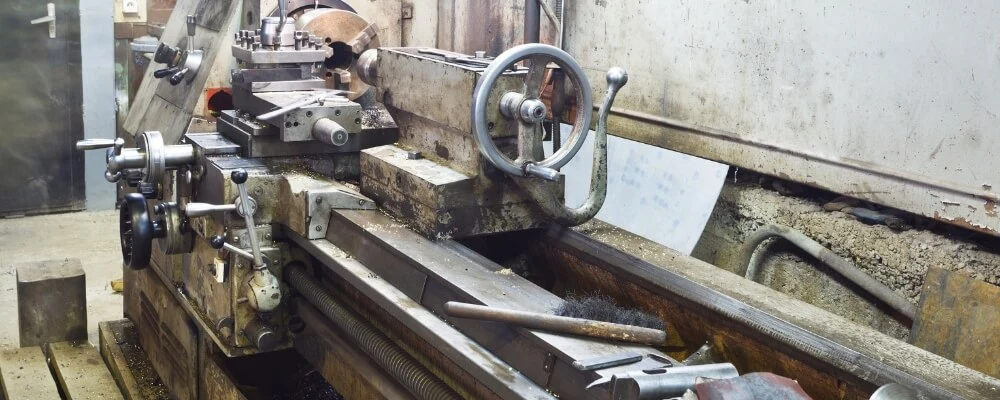

Hierarchy Of Controls For Lathe Machine Hazards
The following is the hierarchy of controls for lathe machine hazards:
- Elimination
- Substitution
- Engineering Controls
- Administrative Controls
- Personal Protective Equipment
1. Elimination
The fundamental premise behind elimination is straightforward: removing a hazard is the most effective way to manage it entirely. In the context of a lathe machine, this might mean discontinuing a particular procedure that’s been identified as especially risky or getting rid of outdated machines that do not comply with modern safety standards.
Elimination ensures that workers are not exposed to the hazard in the first place, thus providing the highest level of protection. However, in many scenarios, especially in manufacturing or production settings, it’s not always feasible to completely eliminate essential processes or equipment. This leads to the exploration of the subsequent tiers of hazard control.
2. Substitution
When direct elimination isn’t viable, substitution serves as a solid alternative. The idea is to replace something hazardous with another with a lower risk. As exemplified, this could mean opting for safer materials in the realm of lathe machines.
If a specific cutting tool or component is identified as hazardous, replacing it with a safer version reduces the inherent risks. It’s vital, however, that the substitution process itself is evaluated for potential new hazards, ensuring that in solving one problem, another isn’t inadvertently created.
3. Engineering Controls
Engineering controls deal with modifying the physical aspects of the workplace to safeguard employees. These are tangible, often structural, interventions that isolate or remove the hazard. Using the lathe machine example, such controls could encompass features like machine guards that prevent accidental contact with moving parts or ventilation systems that effectively extract harmful dust or fumes generated during the machining process.
Another engineering control might include emergency stop buttons positioned within easy reach. These controls target the hazard at its source and aim to mitigate its impact, making the environment inherently safer.
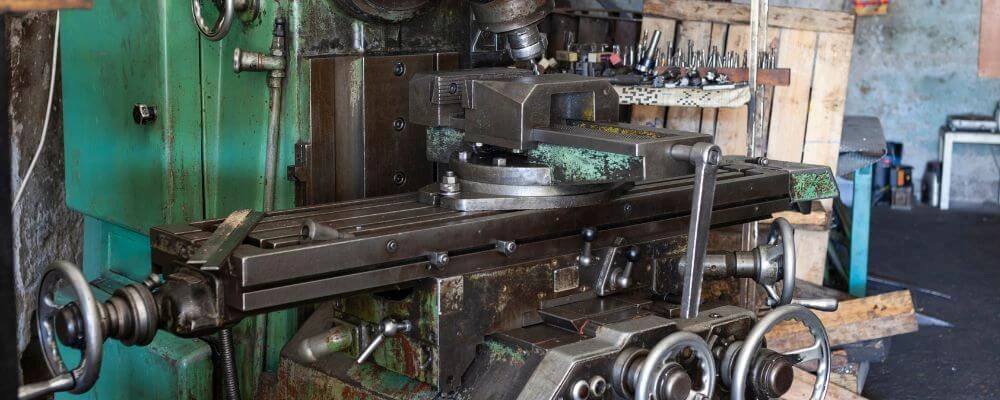

4. Administrative Controls
These controls are more about altering tasks rather than changing physical aspects. Administrative controls often involve implementing new procedures, training programs, or work schedules. For instance, if extended exposure to a lathe machine is risky, shifts might be rotated more frequently, reducing the duration to which any single worker is exposed.
Similarly, comprehensive training sessions can educate operators about best practices, reinforcing the importance of safety protocols. Administrative controls rely heavily on adherence and consistent monitoring, as human behavior largely determines their effectiveness.
5. Personal Protective Equipment
Often considered the last line of defense against hazards, Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is a barrier between the worker and the hazard. When operating a lathe machine, various forms of PPE play crucial roles. Safety goggles or face shields prevent flying debris from injuring the eyes, while earplugs or earmuffs protect against potential hearing damage from prolonged exposure to loud noises.
Gloves can shield hands from burns, cuts, or contact with harmful substances. It’s essential to remember, however, that PPE is to be used in conjunction with other controls and not as the primary or sole means of protection. Regular inspections and maintenance of PPE are also vital to ensure they offer the intended level of protection.
Conclusion
In our exploration of the lathe machine, we’ve traversed its foundational definition, delved into the diverse types tailored for specific applications, and spotlighted the inherent hazards of its operation. Yet, as with any powerful tool, understanding its risks is as crucial as harnessing its capabilities. By adopting the outlined control measures, one can ensure a harmonious balance between productivity and safety.
As we conclude this journey, it’s evident that the lathe machine, a cornerstone of the manufacturing world, is not just a tool but a testament to human ingenuity. By respecting its potential and adhering to safety protocols, we can continue to innovate, create, and pave the way for a safer, more efficient future in machining.