Confined spaces like tanks, sewers, and manholes may be necessary to enter for work, but they’re full of hidden dangers. Think of them like a sleeping beast – they might seem harmless, but one wrong move could wake up a whole world of trouble! That’s why having a rock-solid confined space entry procedure is critical. It’s your map for navigating these hazardous zones, keeping workers safe, and making sure everyone comes home at the end of the day.
Confined Space Entry Procedure
Confined space entry procedures are crucial for ensuring the safety of workers who enter and work in confined spaces. Here’s a general outline of the steps involved:
What is a Confined Space?
Before we dive into the procedure, let’s define a confined space:
- Limited Openings for Entry/Exit: They aren’t designed for someone to work in for long periods.
- Large Enough to Enter: A worker can physically get their body inside to do some task.
- Not Designed for Continuous Occupancy: You wouldn’t spend your whole workday in one.
Examples: Storage tanks, manholes, crawl spaces, sewers, some attics, etc.
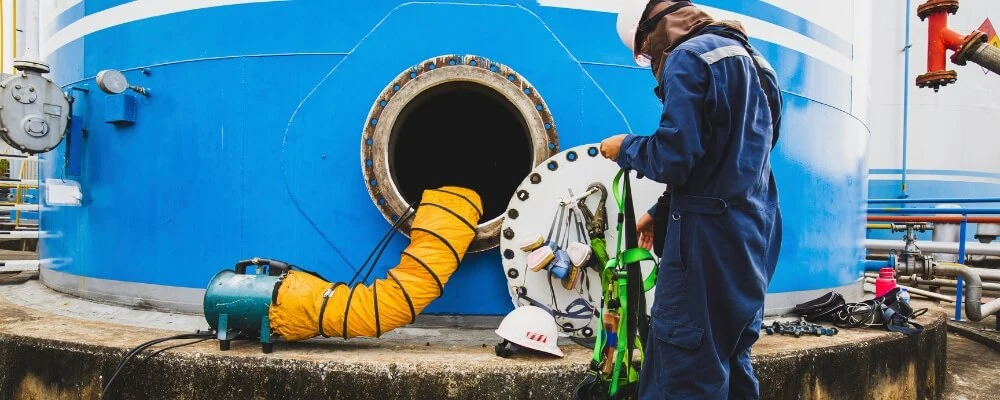

Confined Space Entry Procedure
1. Hazard Identification and Assessment
- Know the Potential Dangers: Before anything, figure out what could be hazardous inside the space:
- Oxygen deficiency or excess
- Flammable gases/vapors
- Toxic atmospheres
- Engulfment hazards (grain, dust, liquids)
- Mechanical or electrical dangers
- History Check: Has anyone been injured in this space before? Learn from past incidents.
2. Prepare the Work Plan
- The Permit: Many locations require a “Confined Space Entry Permit”. This details the hazards, safety equipment needed, who’s authorized to enter, rescue plans, and more.
- Team Roles: Clearly define who is:
- Entrant: Person going into the space
- Attendant: Stays outside, monitors the entrant, handles communication
- Entry Supervisor: Oversees the whole operation, often issues the permit
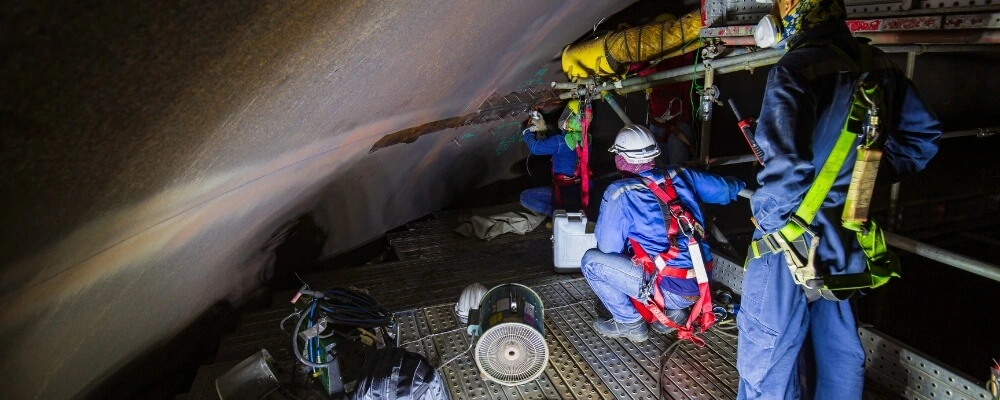

3. Isolate and Secure the Space
- Lockout/Tagout: If there’s machinery, power lines, etc., that could energize while someone’s inside, this MUST be disabled and locked to prevent accidental start-up.
- Block Off the Area: Make sure no one accidentally wanders near the confined space.
4. Atmospheric Testing
- The Right Monitor: You’ll usually use a multi-gas monitor that detects:
- Oxygen levels (should be between 19.5% – 23.5%)
- Flammability (LEL)
- Toxic gases (Hydrogen Sulfide, Carbon Monoxide, etc.)
- Test Before Entry & Continuously: Atmospheric conditions can change fast!
5. Ventilation
- Fresh Air In: If the atmosphere is bad, you’ll need forced ventilation with a fan and ductwork to push clean air in and displace hazardous gases.
- Continue Ventilating: Keep the fan running the entire time someone’s inside.
6. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Respiratory Protection: If the air’s not safe to breathe, entrants will need respirators, often a supplied-air system.
- Harness & Retrieval: Workers need a body harness with a lifeline so they can be quickly pulled out in an emergency.
- Other PPE: Hard hats, safety glasses, protective clothing depending on the hazards in the space.
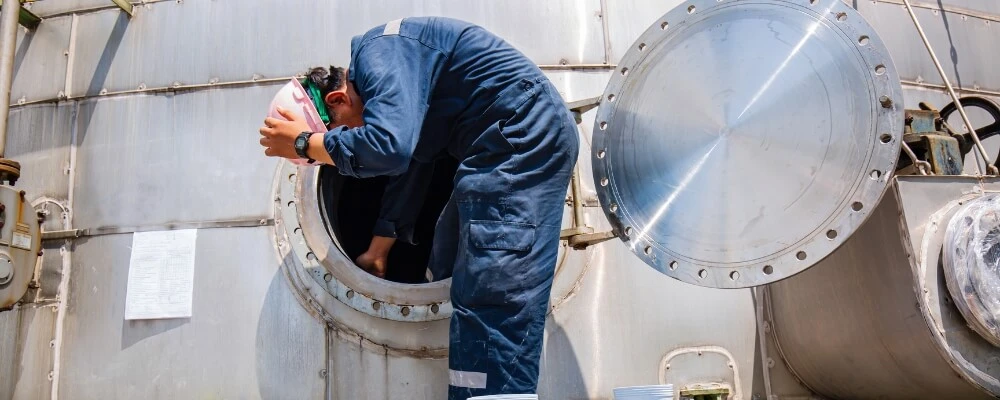

7. Entry and Continuous Monitoring
- Communication Check: Make sure the attendant and entrant can communicate clearly (radios if needed).
- Attendant’s Duties:
- Stay at the space entrance the whole time
- Keep an eye on the entrant, and the atmospheric monitor
- Be ready to raise the alarm, start rescue procedures if needed
- Frequent Check-Ins: Never lose contact with the person inside!
8. Emergency Rescue Plan
- Not Optional: Have a detailed plan for what happens if the entrant gets hurt or the atmosphere turns bad.
- Trained Rescuers: This might be your own team who’ve practiced confined space rescue, or you may need to call the fire department or dedicated rescue service.
Important Notes
- Regulations: Confined space rules vary by location. Make sure you’re following the specific laws in your area.
- Training is Essential: No one should attempt this without proper confined space safety training!
- Re-evaluate Often: Conditions can change. If anything seems off, everyone gets out, and you reassess the situation.